Thit is why we created our advisory trade mark GESOFFICE where, together with Conesa Legal, we believe you can find the best company law advisory in Barcelona.
GESOFFICE is therefore our quality payroll, tax, and company legal advisory firm, located in Barcelona, with Spanish, French and English speaking professionals, eager to help your company to invest or manage your business in Spain, solving all issues that concern the day by day.
We have years of experience advising small, medium, and big-size limited liability companies and autonomous. A team of economists, labor technicians, and lawyers with legal expertise will be able to solve any problem that might concern the company or its CEO.
In us, you will find the confidence and security that we manage your affairs honestly, and with maximum effectiveness guarantees.
Possibly, your best legal advisory firm in Barcelona.
find here a…
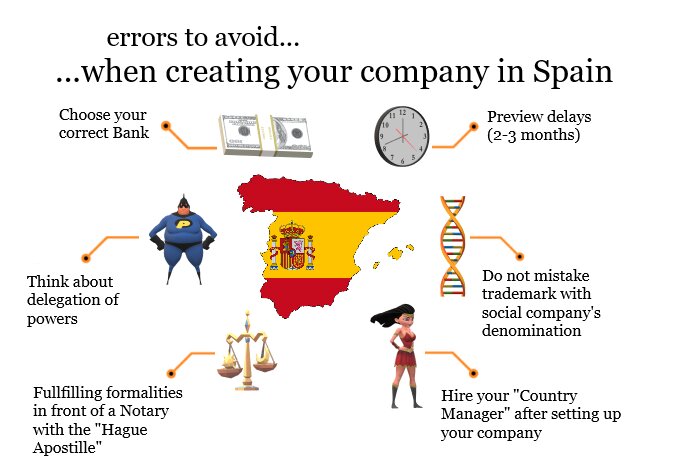
« In vain the lamp burns».
As professionals in legal issues, the experience of creating a company in Spain is “a game that worth the candle” with the good professional companion.
It is with that perspective that we propose to present a complete analysis of principal obligations of a Spanish company, since its constitution to its tax, contractual and employment obligations.
INDEX:
1.- Creating a company in Spain
2.- Tax and accountancy obligations
3.- Labor Law – Eployement Law
4.- Spanish National Insurance
In this case the first bureaucratic stage consists in authenticate certain documents nearby a notary or in front of the Spanish consulate, with also asking for the apostille. The Spanish administration will need company’s bylaws authenticated and apostilled.
But its manager must be also identified by Spanish Ministry of Internal Affairs, who will assign a foreign identification number (N.I.E.) to any person who will reside more than 3 months in Spanish territory, either if he will only perform some activities within Spanish territory.
For this reason it will also be necessary to present the originals of N.I.E. and identity document of the sole shareholder (s) if it is an individual, but also the manager (s), known as “administradores”.
However, depending on the type of activity and the market situation in Spain, we are also able to advise you on the registration of Autoentrepreneur, widespread in Spain, called “Autónomo”. We tell you more in our article “Become a self-employed entrepreneur in Spain”.
The incorporation procedure has an average duration of 2 to 3 months, since each public administration has its own deadline for managing applications for registration and acquisition of mandatory documents.
We facilitate you a list of these minimum mandatory elements:
Once the incorporation procedure has been completed and the company is registered in the Trade Register, it’s important to take into account some additional steps to ensure that the company can operate in accordance with the legislation in force.
Depending on the area of competence, it will be necessary to carry out several burocratic steps in the corresponding administrative bodies.
Almos all companies, if not all, must carry out all administrative procedures via Internet using the “Certificado Digital“. The concept is simple: it is necessary to install on your computer or tablet an “electronic ID” so that you can connect with any public body. It is an indispensable tool, not to say mandatory, for the day-to-day management of your company. We will certainly ask you it if we become your accountant or tax advisor because it facilitates any kind of legal obligation.
The signature of the public grant in front of the Notary does not mark the beginning of your activity.
In addition to the steps to be taken with your company lawyer, your company will have to declare the type of activity and the effective start date in front of the the “Agencia Tributaria Española” (Spanish Tax Administration). For this obligation, you will have to fill through Internet the model for the register of entrepreneurs and professionals census. For the two initial years following your activity start, the Agencia Tributaria also imposes the declaration and payment of the Tax on Economic Activities.
Another important issue is that your company will be required to perform an anually ordinary general meeting, and may be some other extraordinary sessions that the Spanish Company Law obligates if any change at the company. Indeed, during the ordinary session, the administrative body contemplated at the bylaws must meet at least once a year, during the first quarter of each fiscal year, for a very specific purpose: to vote and approve the social management , the annual accounts of the previous year and decide what to do with of the company’s results.
Related to the Book of Minutes, the company is required to update there any amendment related to the shareholders, purchase or sale of shares, and contracts between the sole shareholder and the company, by submitting the corresponding acts to the Register of Commerce of the Region corresponding to company’s adress.
Indeed, we must not forget that the Spanish political system is a decentralized unitary state on a larger scale. In this sense, Spain is divided into 17 Autonomous Communities, themselves divided into Province, then by municipality. These powers and wide enforcement of action to the local authorities allow them to adopt administrative acts specific to their area, always in a respect of compatibility with the principle of identity of the law known as “Estatal” (applicable to all territories belonging to Spain). In this sense, a company whose domicile is in Barcelona or Cornella will be registered in the Mercantil Registry of Barcelona, while a company domiciled in Girona will depend on the Mercantil Registry of Girona, both belonging to Catalonia.
Our team is made up of highly specialized lawyers and economists, especially by Miss. María Teresa GARASA GIL, lawyer, who is in charge of Company Law matters, who will attend you either in English or French, or our tax specialist and economist Mr. David GOMBAU PALAU who will both be able to accompany you in the constitution of your company in Spain.
Do not hesitate to ask them for more information on these steps and their rates for setting up a business in Spain in accordance with Spanish law.
Starting an economic activity within a company involves a whole set of national tax obligations. Some must be done before starting the activity, such as enroll at the contractors and professionals census mentioned previously and others will have to be carried out throughout the activity.
In general, the first step is the presentation of model 036 or 037 of so-called “censal” declaration (census).
Once the activity is started, any income received by natural persons or entities without legal personality is taxed by the personal income tax (IRPF – payments on account and annual declaration). Legal entities are taxed by corporation tax (IS – payments on account and annual declaration).
In addition, obligations related to added value tax (VAT), informative declarations (for example: transactions with third parties – model 347; annual summary of incomes and retentions – model 190, etc.). ) and other mandatory declarations must be completed and declared by Internet.
Being a company means you will have to use use your digital certificate via the Internet to perform any kind of actions with the Spanish administration (review of notifications, response to the administration, tax return, etc.).
In Spain, accounting is the tool on which the tax expert bases himself to calculate, prepare and present company’s taxes.
It is in that sense that the law imposes on employers, regardless of their form of entity (physical or juridic personality) the obligation to keep accounts in accordance with the provisions of Commerce and General Accounting Plan Code or with what is established in the rules to which the obligates is subjected. The Commercial Code requires to have two books of account:
At the Daily Book there should be recorded chronologically, day by day, all the operations carried out in the development of the activity. You can also record total transactions together for periods for a month, but details should be recorded in matching books or similar records.
This book must be opened with the detailed initial balance sheet of the company, retranscribing, at least every quarter, sums and balances, balance sheets. Closing inventory of financial year and annual accounts must be settled annually.
The latest financial statement, at the end of each financial year, contains the annual accounts: balance sheet, income statement, equity statement of changes, cash flow statement and financial position statement . The annual accounts are the most important accounting instrument for corporation tax, as they serve as a starting point for the configuration of your tax base.
In addition to the compulsory books, books and records may be kept voluntarily depending on the accounting system adopted or the nature of their activity.
On the other hand, the is also the obligation to keep and legalize certain “business books”: book of minutes, book of registered shares in anonymous companies and limited shares and registration book associates in limited liability companies.
In addition to the accounting management and the obligatory books of account, it is mandatory to proceed with the legalization of the books of accountancy.
Our team is composed of business management agents, highly specialized economist, especially for business and accounting management like Mme. Eva SERRA ONTIVEROS, specialized in accounting and business law, or like our tax expert and economist Mr. David GOMBAU PALAU and by our lawyer in social and tax law Master Cyrielle AGUT, who can accompany you in English, Spanish or French when dealing with the accounting and tax management of your company.
Don’t hesitate to ask them for more information on these approaches and their management method.
From our experience, we know that many questions arise when hiring staff and often makes business and entrepreneurs feel hesitant.
Labor legal Law is quite different on each country. Regarding Spain, we expose here a summary of the main information concerning the labor contract, the contractual standards, and also the main changes taken in place in recent years .
First of all, let us not forget the very concept of the contract of employment whereby a person undertakes to perform services personally for a fee, within the framework of an organization and under the direction of another person and on behalf of the employer. This is what lawyers call the rule of 5:
Due to the dependency relationship arising from the contract, the labor law seeks to protect the employee against the employer’s arbitrariness, and it tries to rebalance the relations between them, also tryng to organize the company in orther to promote employment.
In accordance with the above-mentioned rule of 5, certain relationships are totally excluded from the system of the Workers’ Statute Law, which is the equivalent of the Labor Code, for the following reasons:
Certain relationships, by their characteristics, will be framed differently and some other particular rules will be applied. they are then treated as an special employment relationships, as provided in Article 2 of Workers’ Statute:Executive officer.
New regulations settle recently in Workers ‘Statute, as the one of 12th May 2019, binds companies to guarantee daily registration of their employees’ working hours, by registering the arrival and departure time of all employees, without prejudice of possible horary flexibility.
This type of information can be collected in any form the company chooses, but respecting the sector, activities and professional categories of employees.
This information must be kept a minimum of 4 years since registration and must be available to employees who would like to have access to it, and also has to be accessible to worker’s legal representatives and the Labor and Social Security Authorities.
Another actual issue that the Spanish legislator has wanted to adopt in work’s world: equal gender opportunities for women and men at their workplaces.
In addition to International and European regulations in this area, the law in Spain recognizes equality between women and men as a universal legal principle, offering legal tools to encourage policies to combat gender inequalities, especially in the context of labor relations where it has become usual to witness sexual harassment, gender harassment or discrimination for pregnancy or maternity.
The Organic Law 3/2007, of March 22, established the necessary behaviors and tools for the effectiveness of gender equality. In particular, this law defines in a concrete way the concepts of sexual harassment, on the grounds of gender or direct sex discrimination:
The official publication of Royal Decree 6/2019 of 1 March of urgent measures in order to guarantee equal treatment and opportunities between women and men marks the introduction of particularly important changes when obligating companies to implement a plan of equality. This regulation provides progressive application of this measure as follows:
This Plan must have a minimum content established by the same Royal Decree, as well as a preliminary and negotiated diagnosis with the wage representation of workers’ structure.
In order to ensure the viability of this internal regulation to the company, it will be necessary for the company to establish what will be the necessary measures to impement, that is to say an action plan. Among these actions, an easy and accessible tool for all employees would be the implementation of an anti-harassment protocol, which includes corrective measures in case of harassment or discrimination.
What are possible causes of a contract ending?
The finalization of the employment contract can be justified based on one of these different causes:
What steps should be taken in case of disputes and with which organization?
Mediation and the necesity to attempt an extrajudicial agreement are also Alternative Dispute Resolutions in force in the Spanish legal system arising ways of solutions among society. Extrajudicial public institutions from the “autonomous” administration favours these non-contentious dispute resolution methods.
Because of this, there are several instruments to avoid conflict in courts, sometimes optional, sometimes mandatory depending on the concept and context of the dispute.
For this purpose there are, for intance, some agreements that are conceived for the maintenance and development of an autonomous system for solving collective social conflicts araised between employers and workers and their representatives. These are sometimes voluntary, somtiemes mandatory, and call trade unions such as UGT, CCOO, CEOE and / or company sindicates like CEPYME o FOMENT to reach agreements named as Autonomous Conflict Resolution (“Acuerdo de Solucion Autónoma de Conflictos”). ). Thiese type of agreements are framed by the Resolution of 10/02/2012 of the Directorate General of Employment.
Another form of extrajudicial dispute management is that provided through the administrative conciliation mechanism. This is a procedure to be fullfilled before subscribing almost any kind of judicial claim in front of Social Courts, other way the Court application will be rejected. The purpose of this approach is precisely to try to achieve a pre-judicial agreement between parties in case of conflict situations such as dismissal, substantial changes in working conditions, claims, etc. In those cases the Social Courts will always have to verify the existence of this attempt of conciliation requiring the conciliation certification act. The “papeleta de conciliación” will have to be handed over for the conciliation administrative body of the place where services were supplied, or person’s concerned address, at the free choice of the person who is making the conciliation request.
Once the “papeleta” has been admitted, the parties will be summoned to appear in front of the public administration that is in charge of conciliations’ management. The parties may be represented by themselves or can use a representative, most often in the case of a lawyer or a “social graduate” (a graduate in social sciences). It is important to know that the absence of the claimer wlll cause the end of the proceeding archiving the initiated file.
Specialists in litigation in labor law and social security in Spain since 1976, our team is built with lawyers registered at the Bar Association of Barcelona (“Ilustre Colegio de Abogados de Barcelona”) who can position in defense of the employer as of the employee.
With us, you have the chance to be represented by Josep CONESA SAGRERA, lawyer and managing partner of CONESA LEGAL, who will also be able to advice you in English; by Maitre Juan Pedro HUERTAS GONZALEZ, specialized lawyer in labor law, collective dispute management and mediator in ” Laboral Court of Catalunya “, by Lola GARCÍA ROMERO lawyer specialized in labor law and human resources; by Lluís PRAT YAGUE lawyer specialized in labor law and social security; or by Cyrielle AGUT lawyer specializing in social and tax law who can also advise you in French, Spanish or English.
Do not hesitate to ask us for any information or either arrange a meeting if you need to explain us your issue.
If you want to take a look to an english version of the Spanish Worker’s Statute you can download at the following link:
Link to download Spanish Worker’s Statute
As in any so-called “social” state, the Social Security organization supervises the social changes at the companies who have the obligation to register any kind of own company or his employees’ movements. According to the Spanish administrative system, the steps of a company with the Social Security are accessible only by forms and models through Internet.
To help you find out about the social security organization system, please find below a summary diagram:
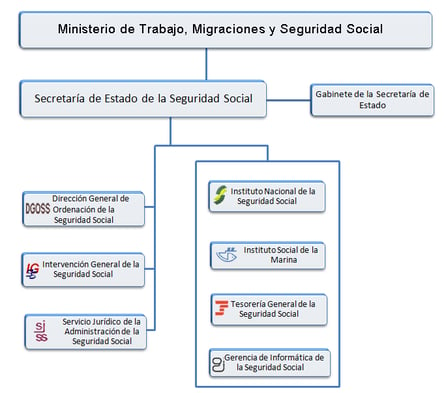
First of all, it is important to specify that the qualification of employer can be used, even if its activity is not motivated by a profit-making purpose, any natural or legal person, public or private, for which salaried workers or employees provide their services on behalf of the employer, provided that these persons are included in one of the contribution schemes set up by Social Security.
Employer’s enrollment withint the Spanish national Social Security system is an administrative act by which the General Treasury of the Social Security gives to the company an identification number, called Contribution Account Code (CCC) and it allows a control of his obligations with the Social Security Scheme.
Depending the province where the entrepreneur will be hire employees he will have to apply for a CCC in that geographical area in order to be directly linked to his main CCC, allowing to link all activities carried out on the Spanish territory. And Social Security may also require the employer to apply for a C.C.C. in specific cases for special workers’ relationshops for which they contributions may be different.
As mentioned above, the company’s registration process as an “employer” falls within the jurisdiction of the Administration of the General Treasury of the Social Security closest to the domicile of the company’s activity. This request can be done electronically through the use of the company’s digital certificate.
In all cases, in case of a young company, before hiring workers, the employer must first ask for his registration as told, before starting his activity. Indeed, the non-registration of the company will make not possible legally hire employees, and consequently, fullfilling necessary contributions of company and employee’s Social Security.
For this, the enrollment file must include the following documents:
1.- In the case of an individual entrepreneur:
Are you preparing to offer a job to potential employees? Remember that before any step, the company must be declared and enrollet at the General Treasury of the Social Security of the Province where the employee will perform his duty.
Regarding procedures they will have to be carried out electronically, taking care of deadlines for registration, termination or employees’ data modifications even salaries of all employees enrollet at the company. That’s ecause Social Security has set up an online electronic network system for professionals and businesses, accessible through your digital certificate, in order to keep a constant eye on the content of your files.
On the other hand, as long as the employment contract between the employee and your company is maintained, you are required to respect the social security obligations derived from the contract. It will not be until the contract is finalized that the obligation to pay benefits and employer contributions will disappear. But this contractual relationship ending will also need to be communicated within the legal deadlines.
As previously stated, a salaried activity rises the obligation to pay social security contribution. That is to say it is born from the moment the worker is enrolled in your company.
However, take notice that the non enrollement of the employee by the corresponding application does not in any way avoid the obligation to contribute to social security obligations if it fits to a labor relationship. In this sense, the General Treasury of the Social Security may ask the company to pay last four year’s duyties of missing enrollment.
This obligation disapears then when finalizating the employment contract, but always conditioned to its ending comjnication. But the obligation of payment will remain in the following cases
With regard to the event of an unpaid amount, the Social Security Administration will set up the existence of the debt in his records resulting from the non-payment of the contributions.
In addition, the Administration will surely require the payment and begin a a process of seizure.
The contribution base in the different schemes of the Social Security system is composed of the total remuneration of the worker, regardless of his form and name.
The contribution base cannot be higher in any case than the maximum limit legally established and fixed by the annual Law of General Budgets of the State. This maximum amount is applicable to all types of activities and / or occupational categories, regardless of the number of worked hours.
In contrast, the legal minimum amount of the contribution base corresponds to the amount applicable to the Minimum Interprofessional Salary in force, increased by one-sixth.
However, some elements cannot be included in the calculation of the contribution base such as:
The calculation of the monthly contribution base is divided into two subgroups:
Hereafter, we detaill an exhaustive list of competences of the public administrations of health according to the steps to realize:
In order to offer you complete support, in addition to legal advice, our Personnel Management Department GESOFFICE are specialized doing all paperwork at the the Social Security and they can explain and manage for you the smoothly way to fullfill of all necessary these steps.
We advise, perform and communicate contracts, enroll employees into the Social Security, we elaborate payslips, adaptating payrolls and contracts to legislative changes and Collective Agreements renewal.
Do not hesitate to contact our social department GESOFFICE composed by Mr. Lluís PRAT YAGÜE lawyer specialized in labor law and social security, Mrs Lola GARCÍA ROMERO lawyer specialized in labor law and social security, Mrs. Judith MONTAÑÉS PARTAL who has a Human Resources degree and she is a specialist in social management and Mrs. Marta VILAR SAURA who is Legal Assistant specializing in social security management.
+34 932 020 256
+34 932 411 174
info@conesalegal.com
Avda. Diagonal 467, 6-1
08036 Barcelona (Spain)
